Common Vision Blox provides a flexible and structured approach to configuring the acquisition stack and connected devices. Configuration is managed through a hierarchical feature tree referred to as Node Map, and individual parameters referred to as nodes. Nodes can be queried and modified by the user.
Device configuration is based on a collection of configurable features, each represented as a node within a node map. Device features are accessed using unique names, which may be defined in the Standard Feature Naming Convention (SFNC). This ensures consistent meaning and behavior across devices from different vendors. Writing to a node will automatically store the changes in the device independently from the transport technology (e.g. USB or ethernet) used.
You can use the GenICam Browser to get an overview over all available nodes. Nodes often contain additional information about a feature like the minimum or maximum value, the unit or even a tool tip.
Quick configuration allows users to provide configuration parameters that are applied during device open. This approach ensures that the device and acquisition stack are configured in an aligned manner, reducing the need for manual adjustments after initialization. While this method is less transparent than direct node manipulation, it can be more convenient for common setups and rapid deployment.
The following options are available independently from the underlying technology. See GigE Vision or USB 3 Vision for technology specific parameters.
| Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| AttachChunk | Enables and attaches chunk data in the device ("0" or "1") | as device |
| UseRdma | Enables RDMA protocols for this device (GEV only) ("0" or "1") | "0" |
| NumBuffer (deprecated) | Number of buffers to allocate for acquisition. Use Cvb::CompositeStreamBase::RegisterManagedFlowSetPool instead. | "3" |
| PixelFormat (deprecated) | Automatically convert the pixel format (see CVB 14.0) | "5" |
| RotateImage (deprecated) | Rotate the memory view on the image buffer (see CVB 14.0) | "0" |
| WidthOverride (deprecated) | Override the image width reported by the device | not used |
| HeightOverride (deprecated) | Override the image height reported by the device. Useful for frame grabbers and line scan cameras. | not used |
Configurations can apply at different level respectively modules of the acquisition stack. Each node map is accessible through a string ID:
Every module of the GenTL can provide a node map with potential features to configure. The above node maps can be explored in the GenICam Browser. In addition, Common Vision Blox introduces two specialized node maps:
Both node maps offer a node map interface but are not actual GenAPI XML node maps. The optimized access to vendor specific features, that are not covered by GenICam.
The VinDevice node map offers users to configure the driver-related device features. Specifically, the node map includes features that are related to TurboDrive feature, or the GenICam chunk data feature. The following list describes all available nodes that belong to the VinDevice node map:
true to the node .true to the node .The VinBuffer node map provides means to gather information about a single buffer returned/delivered by the stream's Wait method call. The VinBuffer node maps the following feature nodes:
true, it indicates that the buffer data is not logically complete. In case of incomplete transmission for some reasons such as missing packets, the number of bytes successfully written to the buffer are reported in the SizeFilled node.The CVB acquisition stack manages the lifetime of all node maps and nodes automatically using a reference counting mechanism. In addition a node will keep the node map alive and the node map will keep its provider alive.
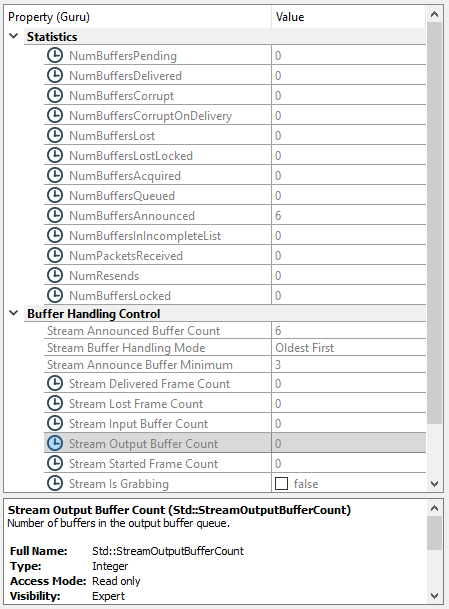
The data stream node map provides both standard and vendor-specific nodes that offer insights into the acquisition engine. These statistics include buffer states, lost packets, and resend requests in the case of GigE Vision (GEV). Monitoring these values helps diagnose performance issues and optimize data flow within the acquisition pipeline.
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| Vin Node Maps | Accessing the Vin node maps. |
| Software Trigger | Configuring and sending a software trigger. |
Getting started with C++
Getting started with .NET
Getting started with Python